Gert Breitfuss, Know-Center, WP2 Economic Aspects and Business Models
The availability of data sources (internal, external, existing, and new) and advances in privacy-preserving technologies (e.g. anonymization, multi-party computation) and artificial intelligence opens up massive business opportunities. It enables companies to develop new data-driven products, services and business models. In order to generate concrete added value from data, the knowledge of how a data-driven service is developed must be built up in the company. A lack of structured value proposition design and a limited understanding of customer needs are challenges in developing data-driven services. Another challenge is the necessary collaboration of different disciplines e.g. data scientists, domain experts and business people. So far few tools are available which facilitate the creativity and co-creation process amongst teams with different backgrounds in the development process of data-driven business models. Therefore we have set ourselves the goal in WP2 to develop or adapt methods and tools that support the development of DDBM. The first tool (Safe DEED Data Map) is a good starting point for checking out the various data sources that can be utilized. The identified data sources can be further processed into a concrete data-driven service by using the Safe-DEED Data-Driven Business Canvas. Finally the Safe-DEED Service Cards are intended as inspiration and creativity support in the entire innovation process.
Following we briefly describe the actual status of 3 different tools we designed and partly tested in the course of the Safe-DEED Project.
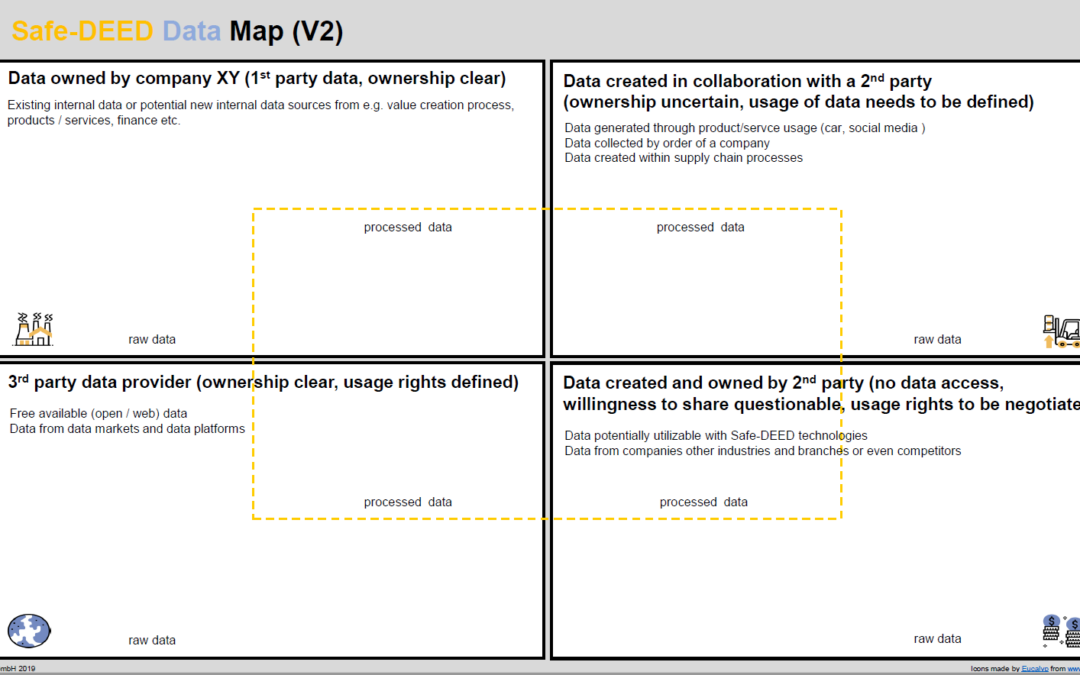
1) Safe-DEED Data Map
Since data is the central resource in a data-driven Business Model we designed a visual collaboration tool to identify possible data sources for developing new data-driven services. The Safe-DEED Data Map is divided into four quadrants. In the first quadrant, we are searching for existing or new internal data (owned by the company). The second quadrant (right-top) is intended for data created in collaboration with a 2nd party (customer, supplier etc.). In the downright quadrant, we look for data that are most interesting for utilizing Safe-DEED technologies, namely data which are created and owned by a 2nd party (no data access, willingness to share questionable and usage rights needs to be negotiated). The last quadrant (bottom left) is reserved for data from 3rd party data provider (free available (open/web) data or data from data markets and data platforms). With the help of the data sources identified by the Safe-DEED Data Map, the development process of data services can be continued.
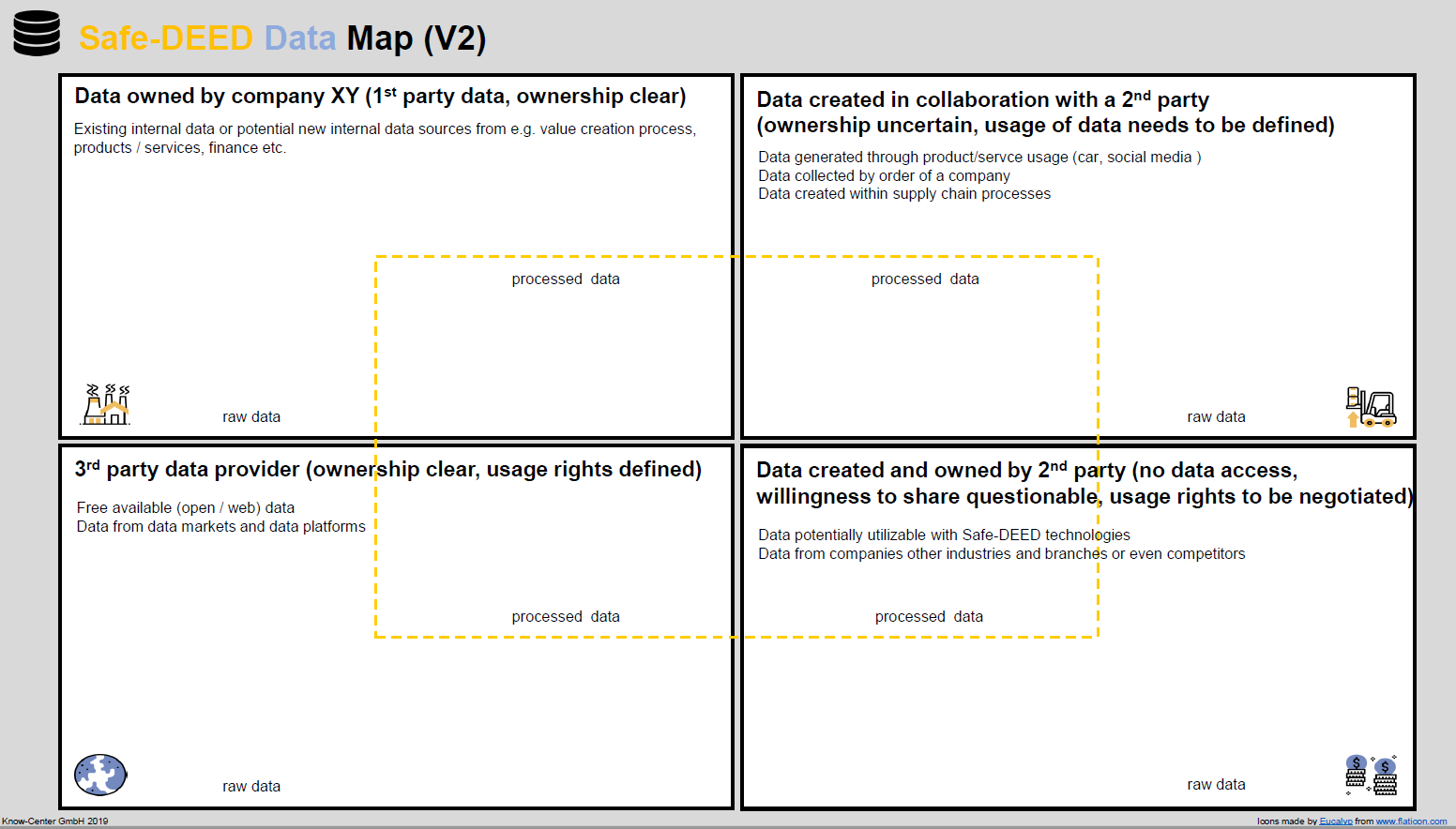
2) Safe-DEED Data-Driven Business Canvas
The Safe-DEED Data-Driven Business Canvas helps to concretise a data-driven use case idea and also includes financial considerations. The canvas consists of five main sections. The data sources (which could be transferred from Safe-DEED Data Map), the needed data analytics or privacy-preserving methods, the representation of the service (e.g. dashboard, API etc.), the intended customer benefit and lastly the financial implications in terms of expected revenues and costs. With all this information a use case is sufficiently specified and should facilitate the implementation of a data- driven business.
3) Safe-DEED Data Service Cards.
To use the tools described above in the best possible way we thought of developing a card-based tool which is commonly used to facilitate creativity and co-creation amongst people with different backgrounds. Therefore we are in the process to develop a set of 40 cards, 10 of each category (Data Sources, Analytics, Data Service and Customer Benefit). The Data Service Cards aim to support the development of new data-based services through inspiration and systematic combination of the cards by using the Safe-DEED Data-Driven Business Canvas.